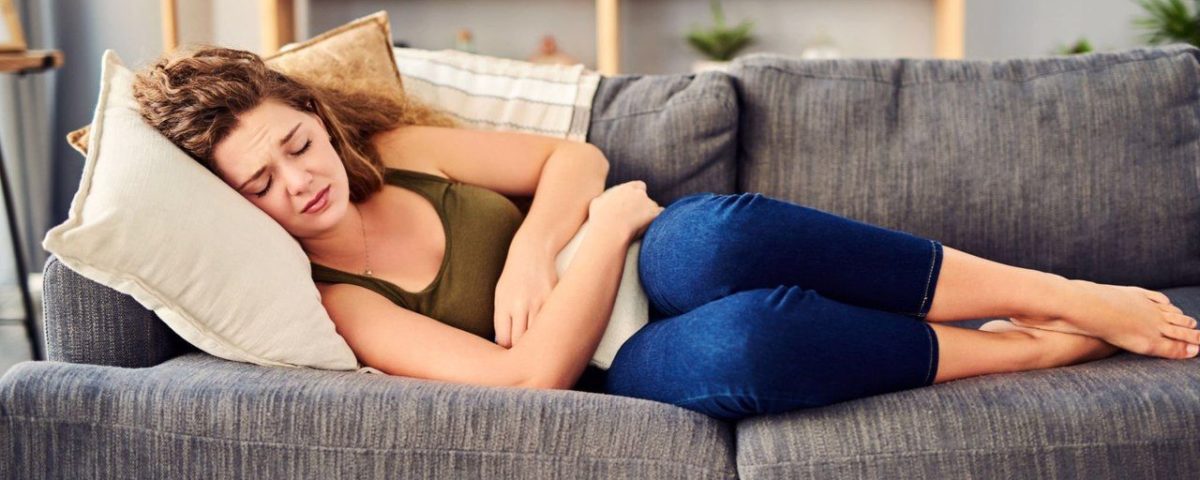
Dysmenorrhea (painful menstruation), experienced by the majority of menstruating women, is cramp-like pain in the groin before or during menstruation. In dysmenorrhea, which can be primary or secondary, primary dysmenorrhea occurs from the first onset of menstruation and diminishes or disappears around the age of 25 or after giving birth. There is no underlying pathological cause of primary dysmenorrhea. However, secondary dysmenorrhea causes painful periods and is usually a precursor to a specific disease.
Causes of Dysmenorrhea
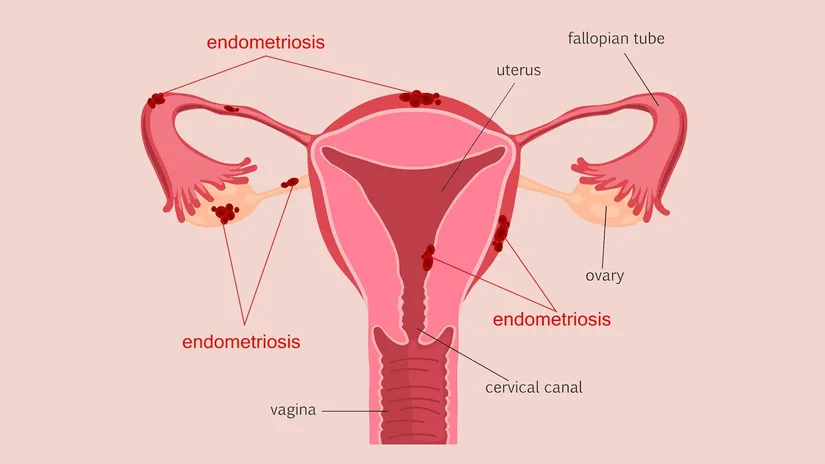
During menstruation, the uterine muscles contract to expel the blood accumulated in the uterus and these contractions cause pain. During these contractions, substances called prostaglandins, which are responsible for uterine contractions, are released. If a woman has primary dysmenorrhea, she has an increased production of prostoglandins. Secondary dysmenorrhea can be caused by problems such as pelvic inflammatory diseases, cervical stenosis, intrauterine tumors (fibroids), endometriosis or abnormal uterine position.
Symptoms of Dysmenorrhea
- Ligament pain
- Back pain
- Nausea – vomiting
- Dizziness
- Hypersensitivity on the inner sides of the legs
On average, 10% or 15% of women with dysmenorrhea have severe symptoms. It is severe enough to affect daily life. If the pain is more severe than usual, lasts more than 2 to 3 days, is not accompanied by menstrual bleeding on normal time and is different from the usual pain, it is absolutely necessary to be checked by a specialist physician to find the source of the problem and to apply treatment.
Dysmenorrhea Treatment
If the pain associated with dysmenorrhea is moderate, it can usually be prevented with painkillers. In such cases (if menstruation is also regular), the person can reduce the intensity of the pain by starting to take painkillers a few days before menstruation, without waiting for menstrual pain to start.
If the menstrual period is characterized by severe pain, then bed rest with hot compresses should be applied to the abdomen. Another treatment method is the use of birth control pills. Birth control pills reduce the prostaglandin substances responsible for pain, which helps to eliminate cramps. Injection painkillers can also be used as a different treatment method when the pain is severe.