Pelvic inflammatory disease, also known as PID. pelvic infection Pelvic pelvic infection is one of the most damaging types of infections affecting the female genital organs. Caused by microorganisms that spread from the vagina or cervix upwards to the upper genital area, pelvic pelvic infection is usually transmitted during sexual intercourse. It can also sometimes occur in women during childbirth, abortion, or as a result of surgery. Multiple sexual partners, intrauterine device use, vaginal douching, AIDS, and bacterial vaginosis are among other factors that can cause pelvic pelvic infection.
Symptoms of Pelvic Infection
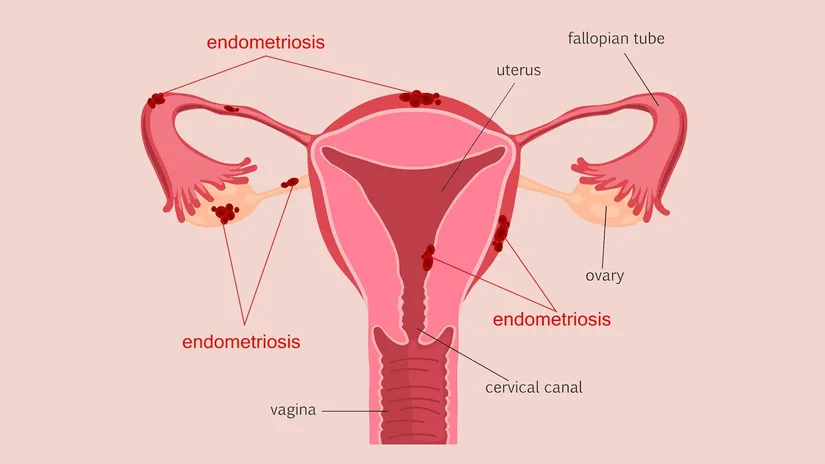
Pelvic pelvic infection, a serious type of infection, occurs in the uterus, fallopian tubes, or ovaries. Affecting the reproductive organs and potentially leading to serious consequences such as infertility if left untreated, some symptoms of pelvic infection are as follows:
- Pelvic and lower abdominal pain
- Vaginal discharge
- Intermittent bleeding and bleeding after intercourse.
- Tenderness during pelvic examination
- Pain during cervical movement
What are the risks of a pelvic infection?
Often mistaken for joint pain, leading to delayed treatment, pelvic infections can cause significant health problems, including infertility and miscarriage, if left untreated. Pelvic infections can also lead to blockages in the fallopian tubes and adhesions between pelvic organs. Sexually transmitted pelvic infections are known as gonorrhea. Besides gonorrhea, chlamydia, mycoplasmas, toxoplasmosis, tuberculosis bacilli, group B streptococci, and IUD use can also cause pelvic infections.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Pelvic Infections
Diagnosis of pelvic infection To make a diagnosis, the patient undergoes physical examination, ultrasound, and laboratory tests. Since pelvic infection can be confused with appendicitis, endometriosis, adnexal mass torsion, ectopic pregnancy, and urinary tract infections, caution is advised during the diagnostic phase, and if the tests are insufficient, laparoscopy should be performed.
Mild to moderate pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) can be treated on an outpatient basis. Patients are usually treated with antibiotics. However, in some cases, surgery (laparoscopic or open surgery) may be necessary. If the infection was transmitted through sexual intercourse, the partner is treated.