Laparoscopy is a type of surgery used in the diagnosis and treatment of various diseases developing in the abdominal region, based on the principle of visualizing the internal abdominal organs. The surgery is usually performed under general anesthesia. A thin telescope is inserted into the abdomen through the patient's navel, and with this method, the internal abdominal organs can be visualized. This surgical method, which aims to determine the causes of various problems such as abdominal pain and infertility, allows for all kinds of gynecological surgical procedures.
What is Laparoscopy and How is it Performed?
Laparoscopy is a surgical procedure used to examine organs and tissues in the abdominal cavity. Also known as minimally invasive surgery, it is performed under general anesthesia by specially trained surgeons. Laparoscopic surgery uses multiple small incisions (0.5 – 1 cm) called ports. A tube-shaped instrument called a trocar, through which special instruments and a camera called a laparoscope pass, is inserted into each incision. At the beginning of the procedure, the patient's abdomen is inflated with carbon dioxide gas to provide a working and viewing field. Images from the abdominal cavity are then transmitted to high-resolution video monitors in the operating room. During the operation, the surgeon can watch the images on the monitor and perform the same procedures as traditional open surgery with fewer incisions.
Because laparoscopic surgeries involve smaller incisions compared to conventional surgeries, patients recover much faster. Additionally, bleeding and pain are significantly reduced, and scarring is smaller. Patients can be discharged immediately after surgery.
When is laparoscopy performed?
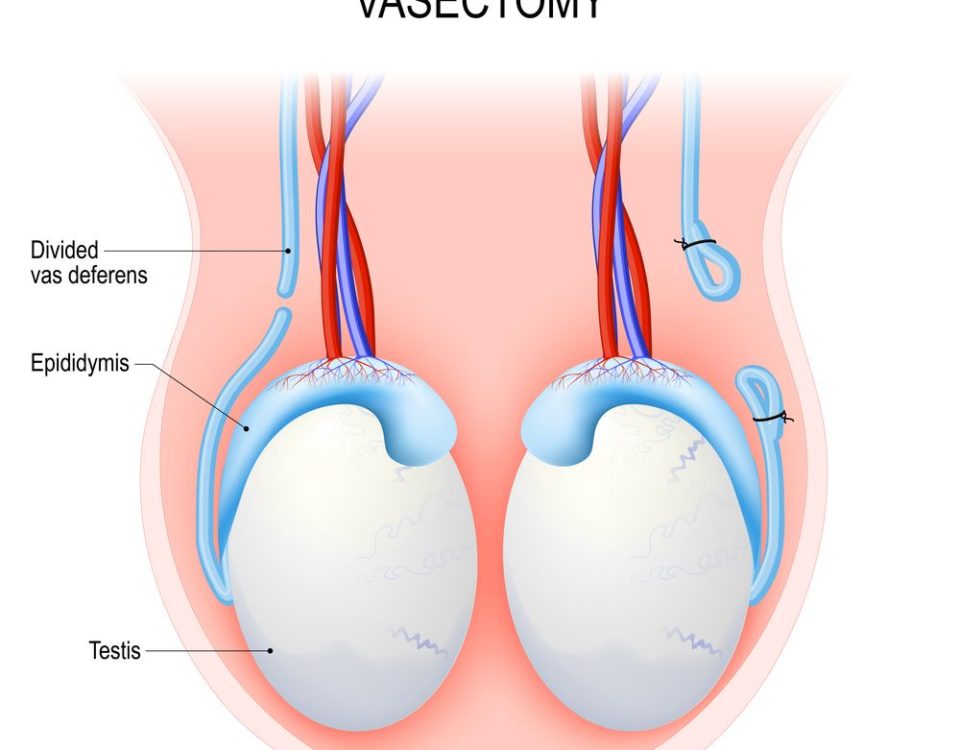
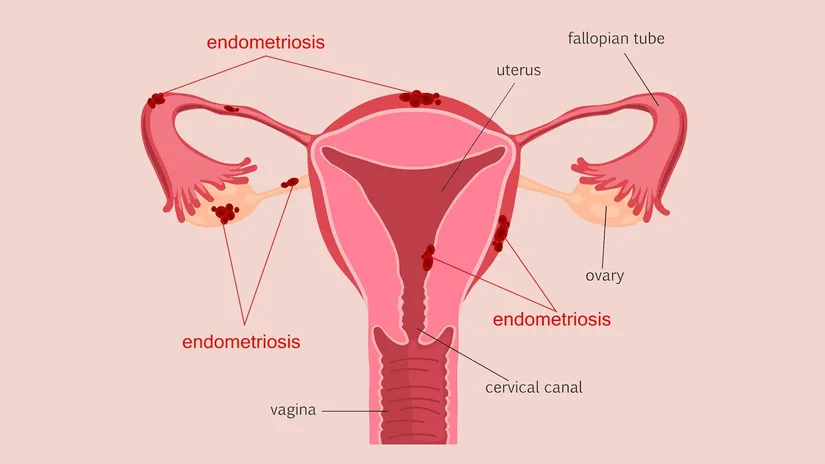
Laparoscopy, primarily used in obstetrics and gynecology, is a method employed in the diagnosis and treatment of many different diseases. In obstetrics and gynecology, it is used to investigate and treat the cause of infertility in women, to overcome and treat uterine problems, to perform hysterectomy (removal of the uterus), and to treat uterine cancer. Laparoscopy can also be applied in cases such as endometriosis, infertility due to ovarian problems, intrauterine adhesions, fibroids, ectopic pregnancy, and to investigate the causes of excessive pain and bleeding during menstruation. Beyond these, laparoscopy can be used in the treatment of cysts or tumors in the abdomen, gallbladder removal, surgical removal of intestines, investigation of persistent abdominal or groin pain, diagnosis and treatment of undescended testicles, hernia repair, and stomach ulcer repair.