Ovarian cancer, one of the most common types of cancer among women, is also one of the cancers that is diagnosed late and therefore causes the most deaths. One or two out of every 100 women develop ovarian cancer, and this type of cancer is fatal. One reason for its dangerous nature is that the disease is often very advanced by the time of diagnosis, and the treatment process is more challenging than for other types of cancer. While more common during menopause, ovarian cancer can occur in women of all ages.
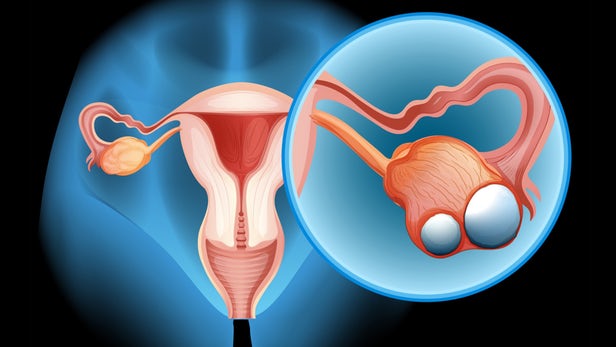
What is Ovarian Cancer??
Ovarian cells are primarily composed of epithelial cells. Uncontrolled division or proliferation of these epithelial cells leads to ovarian cancer. While 80% of % cases of ovarian cancer seen after menopause originate in epithelial tissue, 60% of % cases of ovarian cancer seen in women under 20 are embryonic tumors.
Causes of Ovarian Cancer
- Genetic factors. People with a family history of breast or ovarian cancer have a higher risk.
- The risk is higher in those who use drugs to increase ovulation.
- The risk is higher in women who have never been pregnant.
- Women who use birth control pills have a lower risk than those who do not.
Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer is generally not a type of cancer that shows obvious symptoms, so it doesn't present with clear signs. Symptoms usually vary from patient to patient. In general... symptoms of ovarian cancer Upon examination, symptoms such as bloating, abdominal pain and stomach problems, frequent urination, weight loss, vaginal bleeding, gas, or nausea are observed. In advanced stages of cancer, fluid accumulation in the abdomen, a palpable mass in the abdomen, abdominal swelling, a feeling of pressure downwards from the abdomen, and urinary and bowel complaints are observed.
Ovarian Cancer Diagnosis
Ovarian cancer diagnosis is as important as any other type of cancer. Regular annual routine gynecological checkups are crucial for early detection of cancer.
Ovarian Cancer Treatment
The treatment of ovarian cancer requires collaboration among physicians from different specialties, including gynecologists, oncologists, radiotherapists, chemotherapeuticians, pathologists, dieticians, and psychiatrists. Two different methods are used in the treatment process: surgical and non-surgical. It is a type of cancer that can be treated if diagnosed early. Therefore, I recommend that you have regular annual gynecological checkups and examinations and stay under observation.