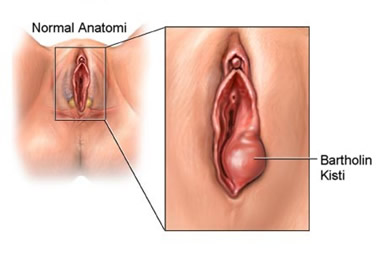
The glands located on both sides of the vagina, inside the labia minora, are called bartolin glands. The bartolin glands, which provide lubrication during sexual intercourse, open into the vagina with thin ducts. The presence of infection or irritation in the area causes blockage of these fine ducts and the secretions cannot be excreted, accumulating in the gland and forming a swelling and cystic structure. If this cystic structure becomes infected for any reason, an abscess is formed. This swelling, called a bartholin abscess, is most common in women of reproductive age who have an active sex life, but it can also be seen in virgin women.
Symptoms of Bartolin Abscess
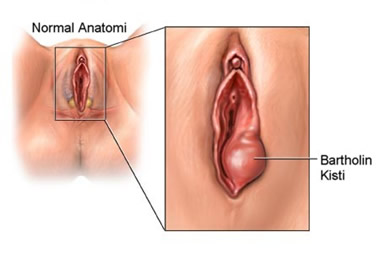 If the bartolin cyst is very small and not yet infected, it may not cause any symptoms. The size of the cyst may remain constant or grow. For example, a small bartolin mass can slowly grow to the size of a tangerine. A bartolin cyst can cause discomfort during sexual intercourse, and when it turns into an abscess, it causes extremely severe pain, redness and swelling at the entrance to the vagina. The pain may be worse when sitting or walking, so the person may have difficulty sitting or walking and may experience great pain. The pain that occurs is very difficult to endure and painkillers may be ineffective in relieving the pain. The pain usually persists as long as the abscess is not drained, but in some cases the abscess bursts spontaneously and the pain decreases.
If the bartolin cyst is very small and not yet infected, it may not cause any symptoms. The size of the cyst may remain constant or grow. For example, a small bartolin mass can slowly grow to the size of a tangerine. A bartolin cyst can cause discomfort during sexual intercourse, and when it turns into an abscess, it causes extremely severe pain, redness and swelling at the entrance to the vagina. The pain may be worse when sitting or walking, so the person may have difficulty sitting or walking and may experience great pain. The pain that occurs is very difficult to endure and painkillers may be ineffective in relieving the pain. The pain usually persists as long as the abscess is not drained, but in some cases the abscess bursts spontaneously and the pain decreases.
Bartolin Abscess Treatment
In some cases, it is necessary to drain the abscess, and sometimes it is necessary to perform a procedure called marsupialization. It may be necessary to use antibiotics for a while after the abscess treatment and in this case it is very important to use your antibiotics regularly. However, if there is a cyst, even if the cyst is opened with a scalpel, the canal is usually blocked again in a short time and cyst formation is observed again in the area. In this case, it may be necessary to remove the barholine gland completely. Bartholin abscess rarely raises suspicion of cancer, especially abscesses that occur at advanced ages should be removed and pathologically examined.