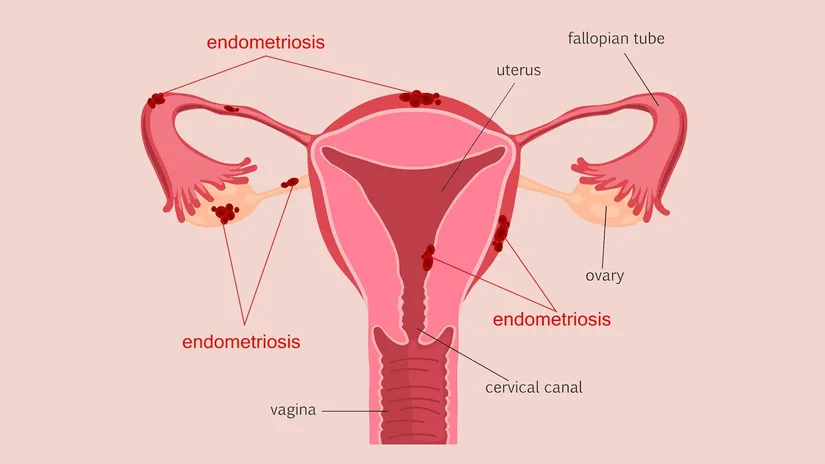
Endometriosis, also known as chocolate cyst, is a condition in which the tissue in the uterus, called endometrium, settles in other tissues. Endometriosis, a chronic disease, develops when the endometrium lining the uterus grows in a different area outside the uterus. Endometriosis, which is usually painful, is most commonly observed in the tissue covering the ovaries, fallopian tubes and pelvis.
What are the Causes of Endometriosis?
Although the factors that cause endometriosis, which can affect women of all ages but is most common in their 30s and 40s, are not fully known, there are some theories about the cause. It is thought that factors such as genetic factors, menstruation in the opposite direction, problems with the immune system, the spread of endometrial cells through the bloodstream or lymphatic system to various parts of the body and settle in various organs may cause this disease.
What are the Symptoms of Endometriosis?
- Painful menstrual period (Dysmenorrhea): Pain that continues for a few days is felt as pelvic pain and cramps. Pain that usually starts before menstruation can also be observed in the lower back and abdomen.
- Pain during sexual intercourse: Pain in the pelvic area can be felt during or after sexual intercourse.
- Pain during defecation or urination: This symptom, which is usually prominent during menstrual periods, can cause pain during defecation or urination.
- Abnormal bleeding Excessive bleeding during menstruation or abnormal bleeding between periods.
- Infertility : Endometriosis can cause adhesions in the abdomen. These adhesions can make it difficult for sperm and egg to meet. It is also thought to cause infertility because it produces natural toxins that kill sperm and prevent the embryo from attaching to the uterus.
Endometriosis Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnostic methods such as pelvic examination, ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and laparoscopy are used to diagnose endometriosis. If the patient is diagnosed with endometriosis, the priority of the treatment is to relieve the pain and to eliminate infertility and enable conception. In the treatment process, drug treatment is tried first, and surgical treatment is preferred if drug treatment fails. If surgical treatment does not result in spontaneous pregnancy, ovulation stimulation and intrauterine sperm implantation can increase the chance of pregnancy.